Page 36 - Surveyor 54.3 and 4
P. 36
PEER REVIEW
PEER REVIEW
The Malaysian Surveyor
practiced method for exploring the which includes work, personal, argues that ethical decisions are
ethical aspects of a decision and professional, governmental, legal and not just individual decisions but are
weighing the considerations that social factors And Trevino’s (1986) determined by the organisation’s
should impact our choice of a course situational-individual model, which social learning. Finally, Brass,
of action. The foundation of ethical includes individual, employment Butterfield and Skaggs (1998) in
decision making involves choice and organizational factors. Rest’s most recent social network model
and balance; it is a guide to discard (1986) of four-component analysis includes individual, organisational,
bad choices in favour of good ones for individual ethical decision making problem-related factors and types
(Hojnacki, 2004). and ethical behaviour is a famous and structures of the ethical
framework for decision making. It decision maker social relationships.
Model of Ethical Decision- comprises four main components: The collection and processing
Making moral awareness, moral judgement, of information within the value
moral motivation, and moral structure and the cognitive limits of
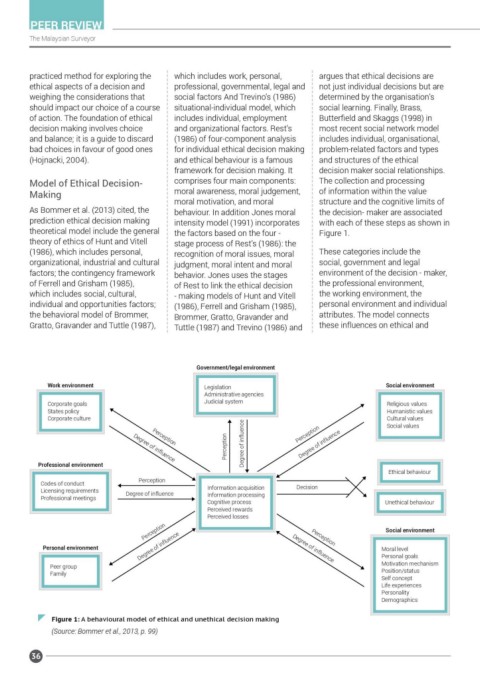
As Bommer et al. (2013) cited, the behaviour. In addition Jones moral the decision- maker are associated
prediction ethical decision making intensity model (1991) incorporates with each of these steps as shown in
theoretical model include the general the factors based on the four - Figure 1.
theory of ethics of Hunt and Vitell stage process of Rest’s (1986): the
(1986), which includes personal, recognition of moral issues, moral These categories include the
organizational, industrial and cultural judgment, moral intent and moral social, government and legal
factors; the contingency framework behavior. Jones uses the stages environment of the decision - maker,
of Ferrell and Grisham (1985), of Rest to link the ethical decision the professional environment,
which includes social, cultural, - making models of Hunt and Vitell the working environment, the
individual and opportunities factors; (1986), Ferrell and Grisham (1985), personal environment and individual
the behavioral model of Brommer, Brommer, Gratto, Gravander and attributes. The model connects
Gratto, Gravander and Tuttle (1987), Tuttle (1987) and Trevino (1986) and these influences on ethical and
Government/legal environment
Work environment Legislation Social environment
Administrative agencies
Corporate goals Judicial system Religious values
States policy Humanistic values
Corporate culture Cultural values
Social values
Degree of influence
Perception Degree of influence Perception
Perception
Degree of influence
Professional environment
Ethical behaviour
Perception
Codes of conduct Decision
Licensing requirements Degree of influence Information acquisition
Professional meetings Information processing
Cognitive process Unethical behaviour
Perceived rewards
Perceived losses Social environment
Perception
Degree of influence Perception
Personal environment Degree of influence Moral level
Personal goals
Peer group Motivation mechanism
Family Position/status
Self concept
Life experiences
Personality
Demographics
Figure 1: A behavioural model of ethical and unethical decision making
(Source: Bommer et al., 2013, p. 99)
36